That is from small molecules containing carbon carbon double bonds.
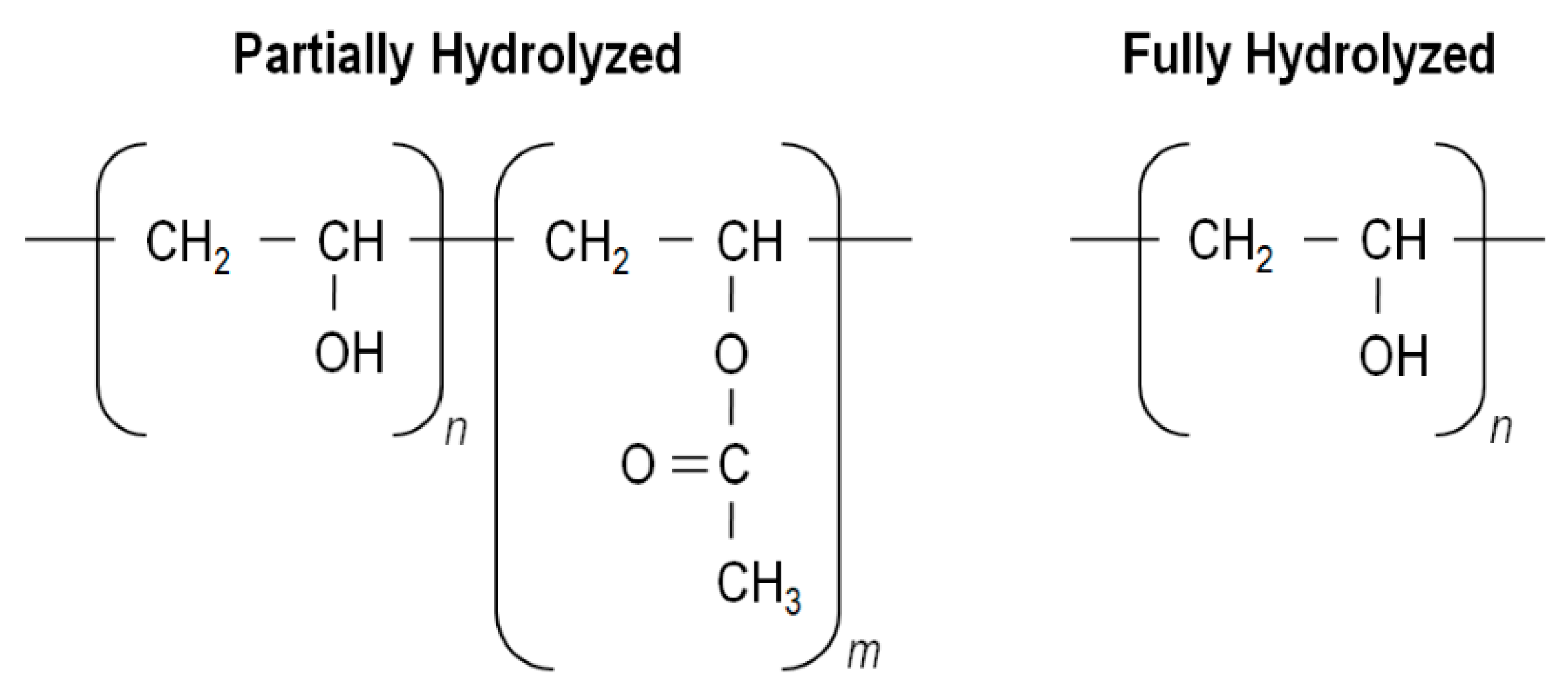
Polymerization of vinyl acetate mechanism.
Contrary to what has been reported.
The mechanism of growth of latex particles in the emulsion polymerization of vinyl acetate using a polymerizable surfactant sodium dodecyl allyl sulfosuccinate trem lf 40.
Kinetic studies and polymerization mechanism d.
Pemberton napier college colinton road edinburgh eh10 5dt uk and.
Mechanisms and techniques 10 1021 bk 2012.
Several aspects of this system have been clarified including the induced decomposition of persulfate retardation by oxygen and entry by and.
Vac can be polymerized only by a radical mechanism.
Vinyl acetate vac is one of the most challenging monomers to work with in preparing polymers with controlled architec tures.
The emulsion polymerization of vinyl acetate was investigated with the use of block copolymers of ethylene and propylene oxides commercially known as pluronic surfactants as emulsifying agents.
The degree of polymerization was.
Zhigang xue rinaldo poli investigation of bis acetylacetonato iron ii as a moderator for the radical polymerization of vinyl acetate progress in controlled radical polymerization.
The bulk polymerization of vinyl acetate in storage vessels occurs spontaneously under constant temperature conditions due to a chemical acceleration phenomenon related to the free radical nature of vinyl acetate chain polymerization.
Both the aqueous phase.
Polymerization of vinyl acetate using visible radiation and a dye reducing agent sensitizer.
It is used to make polymers from vinyl monomers.
Radical polymerization and increases its conversion rate to 95 with a relatively low molecular weight distri bution.
The initiator was azobis isobutyron1trile.
Mechanism of the stabilized radical controlled polymerization of vinyl acetate.
Polymers made by free radical polymerization include polystyrene poly methyl methacrylate poly vinyl acetate and branched polyethylene.
By electron microscopy the.