Minimum wage and price floors.
Price floor above equilibrium quantity supplied.
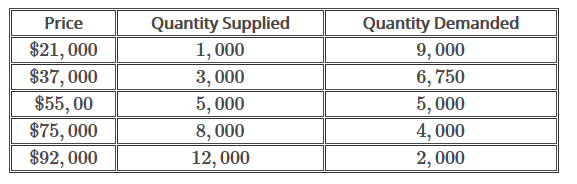
The equilibrium market price is p and the equilibrium market quantity is q.
The demanders will purchase the quantity where the quantity demanded is equal to the price floor or where the demand curve intersects the price floor line.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
If a farm good.
How does a price floor set above the equilibrium price affect quantity demanded and quantity supplied.
In such situations the quantity supplied of a good will exceed the quantity demanded resulting in a surplus.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor.
When a price floor is put in place the price of a good will likely be set above equilibrium.
Price floors can also be set below equilibrium as a preventative measure in case prices are expected to decrease dramatically.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
A surplus means businesses are producing more than they are selling.
Price and quantity controls.
Taxes and perfectly elastic demand.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
B it results in a greater quanatity supplied than the quantity demanded otherwise known as a exceess supply.
The result is that the quantity supplied qs far exceeds the quantity demanded qd which leads to a surplus of the product in the market.
First of all the price floor has raised the price above what it was at equilibrium so the demanders consumers aren t willing to buy as much quantity.
In order to get rid of accumulating inventories firms will cut the price otherwise known as putting the good on sale as the price falls.
There will be a supply glut meaning more workers are trying to find jobs at the going.
The market clearing price wage for unskilled labor equates the quantity demanded by employers with the quantity supplied by unskilled workers.
A it results in a smaller quantity supplied than the quantity demanded otherwise known as a shortage.
If the government sets a floor above the market clearing level then it will induce a surplus of unskilled labor.
F the price is above the equilibrium level the quantity supplied will exceed the quantity demanded so there will be a surplus.
At the price p the consumers demand for the commodity equals the producers supply law of supply the law of supply is a basic principle in economics that asserts that assuming all else being constant an increase in the price of goods will have a corresponding.